As pet owners, we strive to provide our furry companions with the best possible care. Unfortunately, just like humans, dogs can experience various health issues, including kidney injury (KI). Kidney injury in dogs can be a severe condition that requires immediate attention and appropriate diagnostic tools. In recent years, the use of Canine Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) Rapid Test Kit has gained popularity in diagnosing kidney injury in dogs. In this blog post, we will delve into the concept of kidney injury in dogs and explore the utility of the cNGAL Rapid Test Kit.
What is Kidney Injury (KI) in Dogs?

There are two main types of kidney injury in dogs:
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI): This type of kidney injury occurs suddenly and is often caused by a specific event or condition, such as ingestion of toxins, infections, urinary obstruction, dehydration, or a sudden decrease in blood flow to the kidneys. AKI can be reversible if identified and treated promptly. [1]
There are various factors that can lead to acute kidney injury in dogs. Some common causes include Toxins, Old Age, Parasites, Trauma, Cancer, Autoimmune Diseases, Inflammation, Kidney Stones, Genetics, Fungal, Viral and Bacterial Infections.
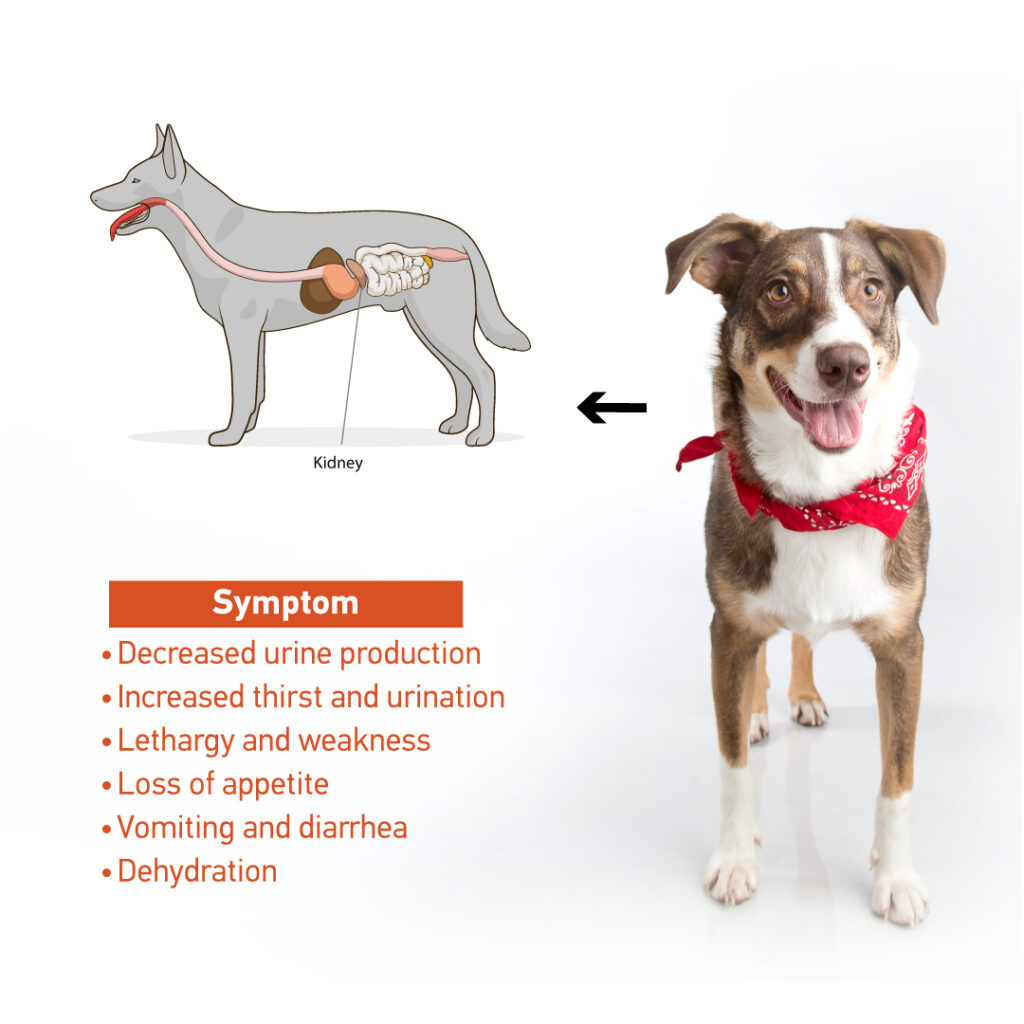
What are the Symptoms of Acute Kidney Injury in Dogs?

The signs and symptoms of acute kidney injury may vary, but common indications include:
- Decreased or no urine production,
- Increased thirst and urination,
- Lethargy and weakness,
- Loss of appetite,
- Vomiting and diarrhea,
- Dehydration,
- Bad breath with an ammonia-like odor,
- Swelling in the limbs or abdomen.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): CKD is a progressive condition characterized by the gradual and irreversible deterioration of kidney function over time. It is usually caused by underlying factors such as congenital abnormalities, immune-mediated diseases, infections, urinary tract blockages, or long-term exposure to certain medications or toxins. [2]
The signs and symptoms of kidney injury in dogs can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Common symptoms may include increased thirst and urination, anemia, bad breath, kidney size changes, loss of appetite, weight loss, lethargy, vomiting, diarrhea, and changes in urine volume or color. [3]
Diagnosis of kidney injury in dogs typically involves a combination of physical examination, blood tests, urinalysis, imaging studies (such as X-rays or ultrasound), and sometimes a kidney biopsy to determine the extent of damage and identify the underlying cause.
Treatment for kidney injury aims to address the underlying cause, manage symptoms, and support kidney function. It may involve fluid therapy to maintain hydration, medication to control blood pressure and manage symptoms like vomiting or diarrhea, dietary changes to reduce the workload on the kidneys, and, in some cases, specific treatments targeting the underlying cause.
Kidney injury in dogs is a severe condition that requires veterinary attention. If you suspect your dog may be experiencing kidney problems, it is essential to consult a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What is cNGAL Rapid Test Kit?
Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) is a protein that plays a significant role in detecting and assessing kidney injury in dogs. NGAL is produced by neutrophils, a type of white blood cell, and is released in response to kidney damage or inflammation.
In healthy dogs, NGAL is present in low levels in the blood and urine. However, when the kidneys are injured or stressed, NGAL production increases and can be detected at higher concentrations. This makes NGAL a valuable biomarker for detecting and monitoring kidney injury in dogs.
There are some traditional analysis methods for NGAL protein, such as serum creatinine level or symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA). However, more than these methods are required. Serum creatinine only changes significantly when about 50% of kidney function is lost. Consequently, serum creatinine may not accurately depict kidney function until several days have passed. Compared to creatinine, SDMA has been found to be a more sensitive indicator of kidney dysfunction. It can detect kidney disease at the stage when 25% of kidney function is compromised. Compared to the delayed detection time of traditional methods, NGAL offers a much shorter timeframe for diagnosing AKI and CKD. An increase in urine NGAL level can allow for a diagnosis within just 2-6 hours. This rapid detection enables healthcare professionals to intervene promptly, significantly improving the prognosis for patients.
The measurement of NGAL levels in urine samples can be performed through laboratory tests or by utilizing cNGAL Rapid Test Kits. These tests allow veterinarians to assess the severity of kidney injury, monitor treatment progress, and make informed decisions regarding the dog’s care.
By incorporating NGAL measurements into the diagnostic process, veterinarians can obtain valuable information about the extent of kidney injury, differentiate between different types of kidney diseases, and guide treatment decisions accordingly. NGAL has shown promising results in research and clinical practice as a reliable biomarker for kidney injury in dogs.
How to Use cNGAL Rapid Test Kit?

The Canine Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin (cNGAL) Rapid Test Kit is a diagnostic tool used to measure the levels of NGAL, a biomarker for kidney injury, in a dog’s urine. Here is a general guide on how to use such a test kit:
Read the instructions: Carefully read and understand the instructions provided with the NGAL rapid test kit. Familiarize yourself with the kit components, storage requirements, and any specific steps or precautions mentioned.
Sample collection: Collect a urine sample from the dog following the instructions provided with the kit.
Prepare the test kit: Open the cNGAL rapid test kit and remove the necessary components. This typically includes test strips or cassettes, buffer solutions, droppers, and sample wells. Ensure that the components are not damaged or expired.
Apply the sample: Place a few drops of the collected urine onto the designated sample well on the test strip or cassette. Be cautious not to exceed the recommended volume.
Add the buffer solution: Using the provided dropper or pipette, add the specified number of buffer drops onto the sample well. The buffer solution helps facilitate the reaction and aids in obtaining accurate results.
Wait for the reaction: As mentioned in the instructions, allow the test strip or cassette to develop for the recommended period. This duration may vary depending on the specific test kit, but it is usually a few minutes.
Interpret the results: After the recommended development time, observe the test strip or cassette for the appearance of colored lines or other indicators. Each kit will have its own interpretation guide, which should be followed precisely to determine the test results accurately.
Record and analyze results: Record the results obtained from the cNGAL rapid test kit, including the presence or absence of lines or indicators. Compare the results with the provided interpretation guide to determine the level of cNGAL in the dog’s urine.
REFERENCES
[1] Cowgill LD, et al. (2019). ACVIM consensus statement: Support for rational administration of gastrointestinal protectants to dogs and cats. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 33(2), 7-18.
[2] Cianciolo RE, et al. (2011). Acute kidney injury: Diagnostic approaches and controversies. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Small Animal Practice, 41(1), 211-224.
[3] Herndon AK, et al. (2018). Biomarkers of renal injury in dogs: A systematic review. Journal of Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care, 28(3), 228-241.